Key Takeaways:
- Build an emergency fund to avoid relying on credit during financial emergencies.
- Create and stick to a budget to manage income and expenses effectively.
- Pay off credit card balances in full each month to prevent high-interest charges.
- Limit unnecessary borrowing and only take on debt for essential needs.
- Plan for significant expenses in advance instead of financing them with credit.
- Increase financial literacy through education and expert advice to make informed money decisions.
Introduction
The Burden of Debt in the U.S.
Debt is a growing issue in the United States, with the average American owing over $90,000 in various forms of debt, including credit cards, student loans, medical bills, and auto loans. While borrowing money is sometimes necessary, excessive debt can severely impact financial stability and well-being. Carrying debt often results in stress, anxiety, and limited financial freedom. Without a plan, debt can quickly spiral out of control, leading to a cycle of borrowing and repayments that is difficult to escape.
Managing debt can be overwhelming, especially when juggling multiple payments with high interest rates. Nonprofit debt consolidation offers a structured way to regain financial stability. In this guide, we’ll explore what nonprofit debt consolidation is, how it works, the types of debts eligible for consolidation, and those not.
What is Personal Debt?
Personal debt refers to the money borrowed by individuals for personal expenses that they cannot pay upfront. This includes credit cards, personal loans, mortgages, auto loans, student loans, and medical bills. While some forms of debt, like mortgages and student loans, can be considered investments in the future, high-interest consumer debt can become overwhelming. Managing personal debt wisely is crucial for maintaining financial security and avoiding long-term financial hardship.
Purpose of This Guide
This guide provides practical, easy-to-implement strategies that help individuals avoid unnecessary debt, manage their finances efficiently, and achieve long-term financial stability. By understanding the common causes of debt and learning how to make smart financial decisions, you can take control of your financial future and work toward a debt-free life.

20 Tips on How to Avoid Debt
1. Establish a Reliable Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a financial safety net, helping you avoid reliance on credit cards or loans when unexpected expenses arise. Sudden expenses, such as medical bills, home repairs, or job loss, can disrupt financial plans. Experts recommend saving at least 3-6 months’ fees in a dedicated savings account. This ensures that you can cover emergencies without falling into debt.
2. Create and Commit to a Practical Budget
A well-planned budget is essential for managing income and expenses. It allows you to track your spending, ensure that you live within your means, and prioritize saving. When creating a budget, categorize your expenses into essentials (housing, groceries, bills), savings, and discretionary spending. Sticking to a budget prevents overspending and helps build financial discipline.
3. Cultivate a Strong Savings Habit
Saving should be a priority, even if you start small. Automating your savings by setting up direct transfers to a savings account ensures consistent contributions. This habit helps you build financial security and avoid unnecessary borrowing in need.
4. Monitor and Manage Your Bills Effectively
Missing bill payments can result in late fees, penalties, and damage to your credit score. To avoid this, set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure bills are paid on time. Maintaining a good payment history helps improve your financial reputation and prevents additional debt accumulation.
5. Differentiate Between Wants and Needs
Many people struggle with debt because they prioritize wants over needs. Before making a purchase, ask yourself if it’s truly necessary or just a temporary desire. Being mindful of spending habits can help you avoid unnecessary debt.
6. Pay Off Your Credit Card Balance Every Month
Credit card debt can become costly due to high interest rates. By paying off your balance in full each month, you avoid accruing interest charges and keep your finances under control. If full payment is not possible, strive to pay more than the minimum to reduce interest expenses.
7. Avoid Lifestyle Inflation
As income increases, upgrading your lifestyle with more expensive purchases is tempting. However, maintaining the same spending habits while earning more allows you to save and invest instead of accumulating debt.
8. Borrow Responsibly and Only When Necessary
Borrowing should be a strategic financial decision, not a habit. Before taking out a loan or using a credit card, assess whether the expense is essential and whether you can afford the repayments. Avoid borrowing for non-essential purchases, such as vacations or luxury items.
9. Build and Maintain a Healthy Credit Score
A good credit score (typically above 700) qualifies you for better loan terms and lower interest rates. Keeping your credit utilization low, paying bills on time, and regularly checking your credit report for errors can help maintain a strong credit profile.
10. Track Small Expenses – They Add Up!
Small, daily expenses—like coffee, snacks, or ride-sharing—may seem insignificant, but they can quickly drain your budget. Tracking these “invisible” costs helps you identify where to cut back and avoid unnecessary debt.
11. Be Mindful of Buy Now, Pay Later Offers
“Buy Now, Pay Later” services may seem attractive but often lead to overspending and financial strain. These payment plans can create an illusion of affordability while accumulating hidden fees and interest. Before using such services, ensure that you can make payments on time.
12. Avoid Impulse Purchases
Impulse purchases can quickly deplete your budget and lead to unnecessary debt. Practicing the 24-hour rule—waiting a day before making non-essential purchases—can help determine whether an item is a genuine need or an impulsive desire.
13. Limit Your Credit Card Use
While credit cards offer convenience and rewards, overusing them can lead to high-interest debt. Using cash or a debit card for everyday purchases can help you stick to your budget and avoid accumulating unnecessary credit card debt.
14. Plan for Large Expenses in Advance
Rather than financing big-ticket items with credit, save up beforehand. Whether planning a vacation, buying a car, or upgrading your home, setting aside money in advance reduces reliance on loans and credit cards.
15. Be Wary of Co-Signing Loans
Co-signing a loan makes you legally responsible for the debt if the primary borrower fails to repay. This can negatively impact your credit and finances. Only co-sign if you are financially prepared to cover the loan yourself.
16. Learn About Interest Rates and Loan Terms
Before taking on debt, compare interest rates, repayment terms, and total costs. High-interest, payday, and predatory lending practices should be avoided, as they can lead to long-term financial struggles.
17. Increase Your Income and Reduce Unnecessary Expenses
Boosting your income through side jobs, freelancing, or career advancements can help improve financial security. Simultaneously, reducing unnecessary expenses like subscriptions, eating out, and impulse shopping can free up money for savings and debt repayment.
18. Seek Financial Education and Advice
Financial literacy is crucial for making informed decisions. Reading personal finance books, following reputable financial blogs, or consulting a certified financial advisor can provide valuable insights into managing money effectively.
19. Negotiate Your Bills and Expenses
Many people don’t realize they can negotiate bills such as cable, internet, insurance, and even medical expenses. A simple phone call asking for a lower rate, discounts, or payment plan options can save money and reduce financial strain.
20. Set Spending Limits for Special Occasions
Holidays, birthdays, and celebrations can lead to excessive spending. Set a budget for gifts, parties, and travel to avoid going into debt for temporary moments. Thoughtful planning ensures you enjoy these occasions without financial regret.
How to Pay Off Debt
Paying off debt requires a strategic approach.
Start by listing all your debts, including balances, interest rates, and minimum payments. This helps in creating a structured repayment plan.
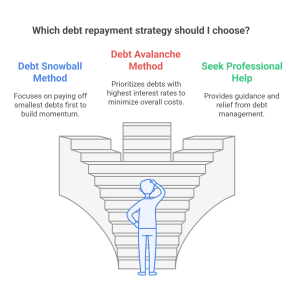
Next, choose a repayment strategy. The Debt Snowball Method focuses on paying off the smallest debts first, while the Debt Avalanche Method prioritizes debts with the highest interest rates to minimize overall interest payments.
Making extra payments whenever possible, negotiating lower interest rates, and avoiding new debt while repaying existing obligations can accelerate debt elimination. If you feel overwhelmed, seeking professional help from a credit counseling agency or financial advisor can provide relief and guidance.
Making extra payments whenever possible, negotiating lower interest rates, and avoiding new debt while repaying existing obligations can accelerate debt elimination. If you feel overwhelmed, seeking professional help from a credit counseling agency or financial advisor can provide relief and guidance.
Conclusion
Avoiding debt requires financial discipline, planning, and wise spending habits. Key strategies include building an emergency fund, budgeting, saving regularly, and making informed borrowing decisions.
By implementing these tips, you can start your journey toward financial freedom. Make a budget, set financial goals, and take proactive steps to secure a debt-free future.
For more financial guidance, visit:
- National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC) – www.nfcc.org
- Federal Student Aid – Loan Repayment – studentaid.gov
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) – www.consumerfinance.gov



