Key Takeaways
Debt Collection Regulations – The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) protects consumers from unfair debt collection practices.
Required Disclosures – Debt collectors must provide a validation notice within five days, detailing the creditor’s name, debt amount, and dispute rights.
Consumer Rights – Consumers can dispute debts, request written verification, and stop communication if needed.
Prohibited Practices – Harassment, misleading claims, and unfair tactics are illegal.
Digital Age Considerations – Electronic communications must follow strict privacy and security regulations.
Best Practices – Consumers should document interactions, verify debts, and report violations to regulatory bodies.
Debt collection communications play a crucial role in the financial system, ensuring creditors can recover unpaid debts while protecting consumers from unfair practices. However, due to the potential for abuse and misinformation, these communications are heavily regulated under laws such as the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA). This blog provides a comprehensive overview of debt collection communications, covering the legal framework, consumer rights, prohibited practices, and best practices for managing interactions with debt collectors in the modern digital age.
Legal Framework and Regulations
Debt collection is a highly regulated activity to prevent harassment, abuse, and unfair practices against consumers. The FDCPA, enacted in 1977, establishes clear rules for how debt collectors communicate with debtors. Additionally, regulations such as the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) rules and state-specific laws impose further compliance requirements.
The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA)
The FDCPA applies to third-party debt collectors and outlines rules that protect consumers from deceptive and aggressive collection tactics. Some key provisions include:
- Restrictions on communication: Limits when and how debt collectors can contact consumers.
- Prohibition of harassment: Prevents threats, abusive language, or repeated calls meant to intimidate.
- Consumer rights: Allows individuals to dispute debts and request verification.
- Enforcement measures: Provides legal recourse against violations, including lawsuits and financial penalties.
Modern Communication Channels
With technological advancements, debt collectors now use multiple channels to reach consumers, including:
- Phone calls (traditional yet still widely used)
- Emails and text messages (regulated under the CCFPB’snew debt collection rule, effective since 2021)
- Social media messages (subject to strict privacy and disclosure rules)
- Letters and official notices (still a legal requirement in certain situations)
While modern communication offers convenience, it also raises concerns about privacy, security, and consumer protection, which are addressed under digital debt collection regulations.
Required Disclosures and Notifications
Debt collectors must provide specific disclosures to ensure transparency. These include:
Initial Communication Requirements
Debt collectors must identify themselves and state they are attempting to collect a debt. The consumer must also be informed that any information provided will be used for debt collection.
Validation Notice: Ensuring Transparency in Debt Collection
A validation notice is a critical requirement under the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA), ensuring consumers receive accurate information about their debts. Within five days of the initial contact, debt collectors must send a written validation notice to the debtor. This notice must include:
- The Name of the Creditor – The official entity or financial institution to whom the debt is owed. This helps consumers verify the legitimacy of the claim.
- The Amount of Debt – A clear and itemized breakdown of the outstanding balance, including any fees or interest added.
- Dispute Information – Instructions on how the consumer can dispute the debt. The debtor has 30 days to challenge its validity.
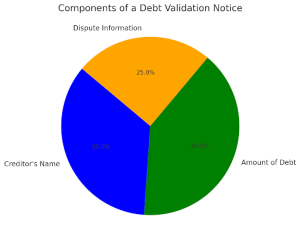
Validation Notice
If a consumer disputes the debt within 30 days, the collector must pause collection efforts until the debt is verified. This prevents erroneous or fraudulent collections.
Failure to provide a validation notice can lead to legal consequences for the debt collector, including lawsuits and regulatory penalties. Consumers should review this notice carefully, request further validation if needed, total national debt, and never pay an unverified debt. Ensuring compliance with this requirement promotes fairness and transparency in the debt collection.
Consumer Rights and Protections
Under the FDCPA and related laws, consumers have significant protections. Understanding these rights is essential to preventing unfair treatment and abuse.
Right to Cease Communication
Consumers can request in writing that a debt collector stop contacting them. Once the request is received, the collector can only contact the consumer to:
- Confirm they will no longer contact them.
- Inform them of legal actions being taken regarding the debt.
Dispute Rights
If a consumer disputes a debt within 30 days of receiving the validation notice, the collector must cease collection efforts until the debt is verified. The collector must then provide:
- Written verification of the debt
- The original creditor’s name and address
If a debt cannot be verified, the collector must stop attempts to collect it.
Prohibited Practices
Debt collectors must operate within legal and ethical boundaries. The FDCPA explicitly bans the following practices:
Harassment or Abuse
- Repeated calls intended to annoy or harass
- Use of threats, obscene language, or intimidation tactics
- Calling at odd hours (before 8 a.m. or after 9 p.m.) without permission
False or Misleading Representations
- Claiming to be an attorney or government official
- Misrepresenting the amount owed
- Threatening legal action that is not intended
- Falsifying documents to mislead the consumer
Unfair Practices
- Attempting to collect unauthorized fees
- Depositing post-dated checks early
- Publicly disclosing consumer debts (e.g., via postcards or social media)
Best Practices for Consumers
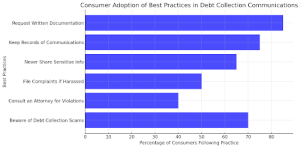
Understanding and implementing best practices in debt collection communications is essential for protecting consumer rights. The graph highlights that 85% of consumers request written documentation, ensuring they have proof of debt legitimacy. 75% keep records of communications, which serve as evidence in disputes. However, only 50% report harassment, indicating a need for greater awareness. While 65% avoid sharing sensitive information, scams remain a concern. Legal consultation (40%) is underutilized, possibly due to cost concerns. Strengthening consumer education on filing complaints and seeking legal aid can enhance protection against unfair collection practices, ensuring transparency and fairness in debt-related communications.
Responding to Collection Communications
- Always request written documentation before agreeing to pay.
- Keep records of all communications, including emails, phone calls, and letters.
- Never share sensitive information (e.g., Social Security numbers) unless the collector is verified.
Protecting Your Rights
Debt collection laws provide consumers with essential protections against harassment and deceptive practices. If you experience aggressive collection tactics, take the following steps to safeguard your rights:
- File a Complaint: If a debt collector harasses or misleads you, file a complaint with the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). These agencies investigate violations and take action against unlawful debt-collection practices.
- CFPB Complaint Portal: Submit a Complaint
- FTC Complaint Portal: Report a Scam
- Seek Legal Help: If you believe your rights have been violated, consult an attorney specializing in Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) cases. Legal professionals can help you take legal action and recover damages.
- Beware of Scams: Fraudsters often attempt to collect non-existent debts. Always request written verification and avoid sharing personal or financial information with unverified collectors.
Table: Key Actions to Protect Your Rights
| Action | Description | Useful Link |
| File a Complaint (CFPB) | Report unfair or aggressive debt collection practices | CFPB Portal |
| File a Complaint (FTC) | Report scams and fraudulent debt collectors | FTC Portal |
| Consult an Attorney | Get legal help if your rights are violated | Find Legal Aid |
| Verify Debt Legitimacy | Always request a written validation notice before paying | – |
Digital Age Considerations
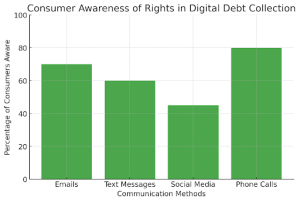
With the shift toward electronic debt collection, consumers of loans for high credit utilization must stay informed about their rights regarding digital communications. Debt collectors now use emails, text messages, social media, and phone calls to reach debtors. However, awareness levels vary across these platforms, as shown in the graph.
- 70% of consumers understand their rights to email communications, while only 45% are aware of social media regulations.
- Phone calls remain the most understood channel (80%), but digital interactions raise privacy and security concerns.
- Consumers should always verify the legitimacy of digital communications, opt out if desired, and report any violations.
Digital Age Considerations
Electronic Communications
Debt collectors can use email, text messages, and social media to reach consumers but must follow these rules:
- Identify themselves as debt collectors.
- Provide an opt-out option for digital communications.
- Keep messages private (e.g., no public social media posts).
Privacy and Security
- Avoid sharing debt details on unsecured platforms.
- Verify the legitimacy of digital communications before responding.
- Beware of phishing scams impersonating legitimate debt collectors.
The Bottom Line
Debt collection communications are a necessary part of financial systems, but they must comply with strict legal guidelines to protect consumers. The FDCPA and modern regulations ensure transparency, fairness, and consumer rights. Understanding required disclosures, dispute rights, and prohibited practices empowers consumers to manage debt collection interactions effectively.
By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can avoid deceptive tactics, should I limit myself to a daily budget, respond confidently, and safeguard their financial well-being.
By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can avoid deceptive tactics, limit themselves to a daily budget, respond confidently, and safeguard their financial well-being.



